In the windswept desert of Argentina, a shepherd’s discovery in 2014 revealed a prehistoric giant that redefined what we thought possible. Beneath the ground lay the remains of a titanosaur, a creature so massive it dwarfs all known dinosaurs. At 121 feet long and weighing 70 metric tons, this herbivore’s fossils have rewritten the history of Earth’s ancient giants.
The Discovery at La Flecha Farm
The journey began when a shepherd noticed the tip of a colossal fossilized bone protruding from the ground. His report reached paleontologists at the Egidio Feruglio Palaeontology Museum (MEF) in Trelew, Argentina, sparking an excavation effort that would span years. Led by Dr. Diego Pol, a team of experts set up camp at the remote site to unearth what turned out to be a paleontological treasure trove.
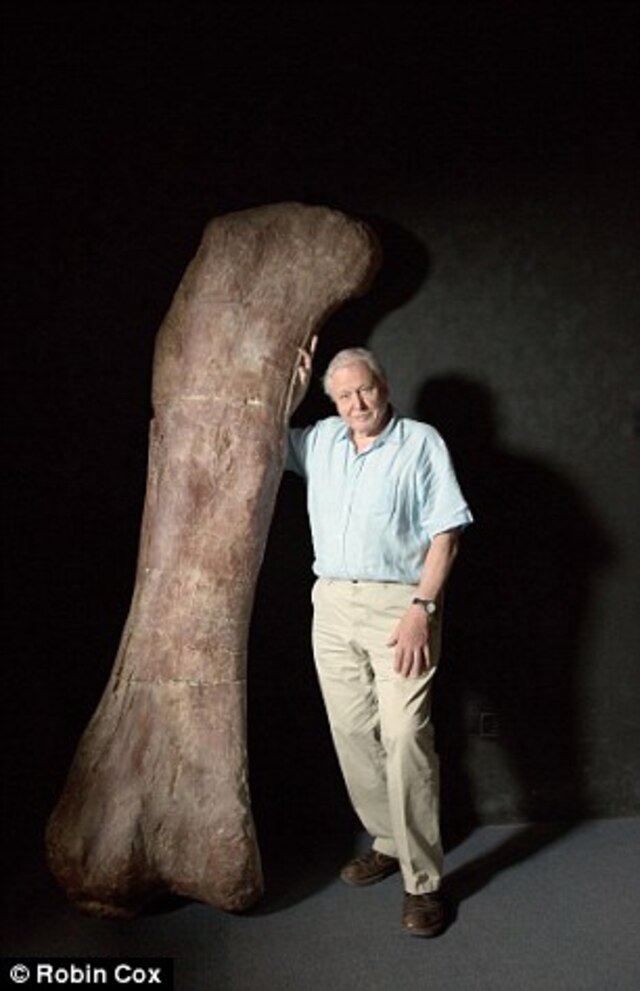

In an upcoming documentary, Sir David Attenborough will narrate the remarkable discovery in Argentina, unveiling how this gentle giant, which lived 102 million years ago, might have appeared.
The first major find was an eight-foot-long femur, the largest ever discovered. By the end of the dig, over 220 bones and 80 teeth were recovered, all belonging to a new species of titanosaur. The exceptional number and condition of the fossils allowed researchers to reconstruct the dinosaur with unprecedented accuracy, revealing it to be 10% larger than Argentinosaurus, the previous record-holder.
Video:
The Newly Discovered Titanosaur
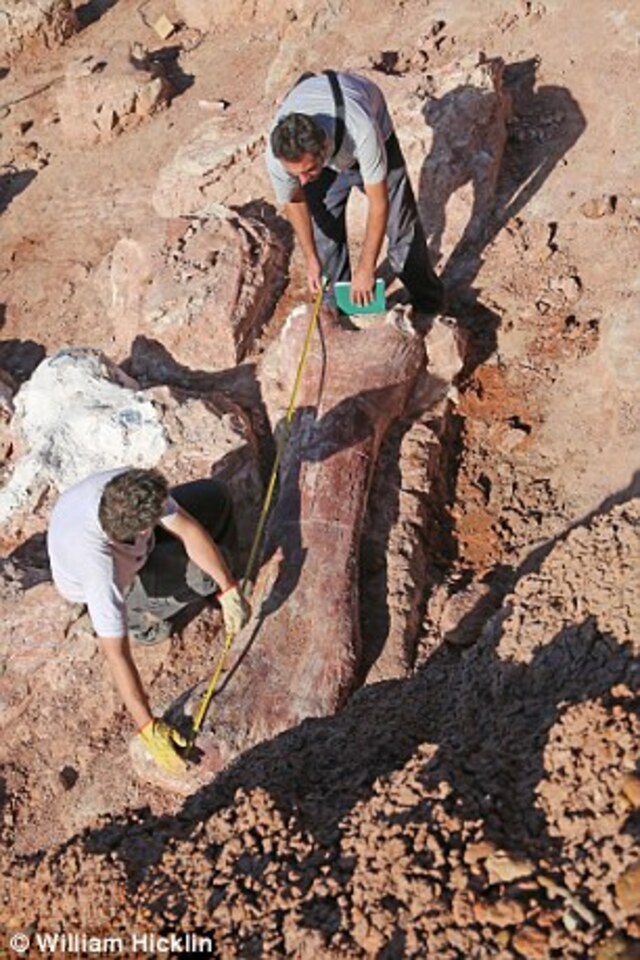

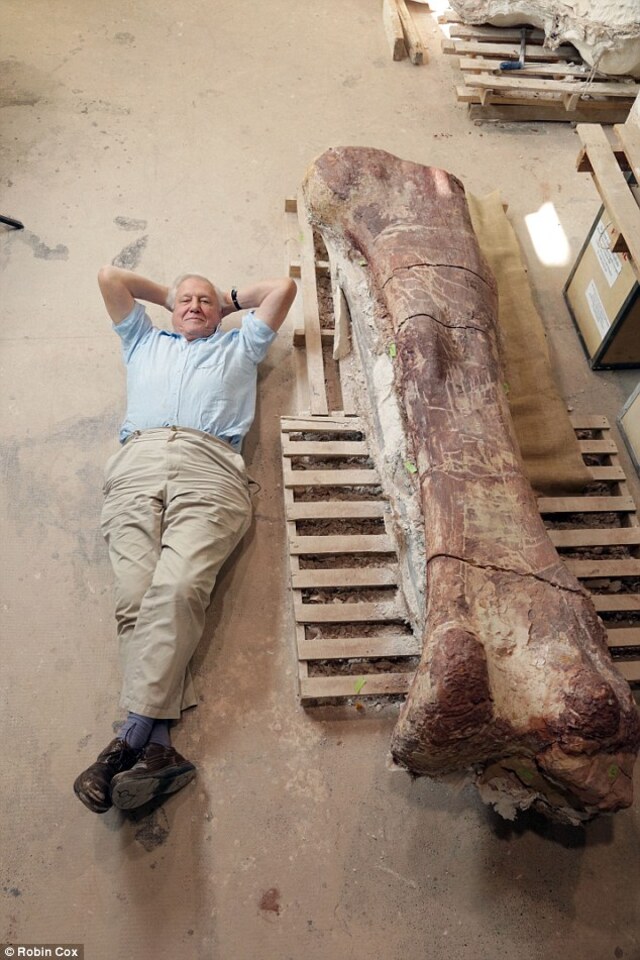
The first unearthed bone was an incredible eight-foot (2.4-meter) thigh bone, the largest ever discovered.
This unnamed titanosaur represents the pinnacle of size in terrestrial life. Measuring 121 feet in length—equivalent to four double-decker buses—and weighing as much as 14 African elephants, the creature dwarfs other known dinosaurs. Its heart alone, estimated to weigh as much as three adult humans, would have been six feet in circumference, capable of pumping 158 pints of blood with a single beat.
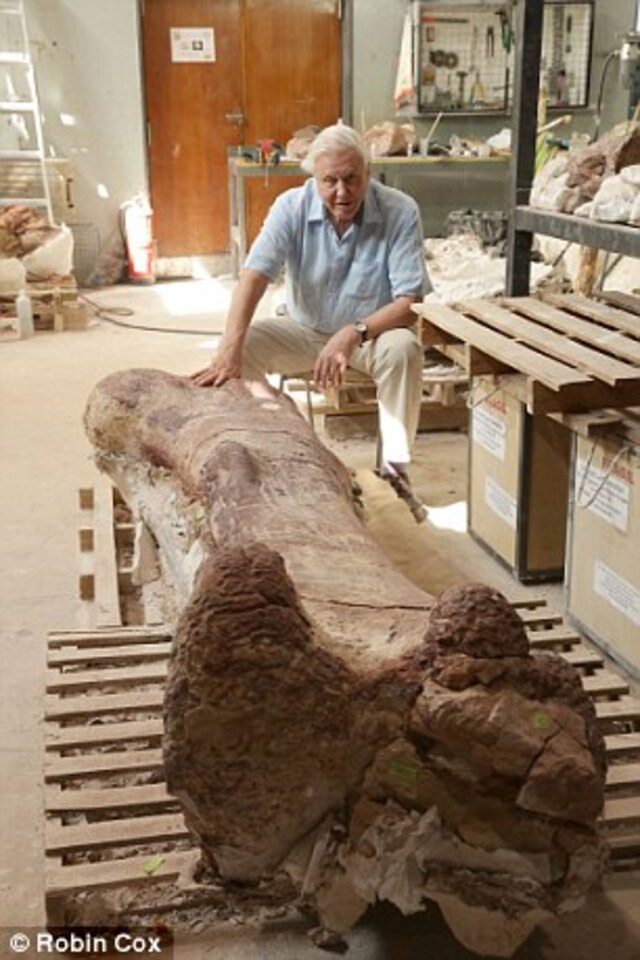

The monumental thigh bone, measuring eight feet (2.4 meters), set a record as the largest fossilized bone ever found.
The dinosaur’s diet consisted entirely of plants, requiring it to consume vast amounts of vegetation daily. Its massive gut, akin to a natural fermentation chamber, slowly digested its meals to extract the nutrients needed to sustain its colossal body. Despite its immense size, the titanosaur’s skeleton reveals an elegant design optimized for weight distribution, allowing it to move efficiently across the ancient landscape.
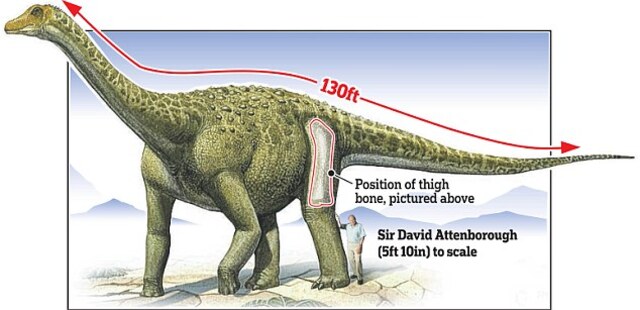
Dwarfing even the massive Diplodocus, the titanosaur measured an astonishing 36 feet (11 meters) longer—comparable to the length of four double-decker buses. A graphic illustrates Sir David Attenborough’s size beside the prehistoric behemoth.
Exceptional Features of the Discovery

Analysis of the leg bones suggests these titanosaurs were still growing young adults, indicating that a fully mature specimen would have been even larger. Unlike Argentinosaurus, which was reconstructed from only a dozen bones, this dinosaur’s size has been measured with far greater precision.
What makes this discovery particularly exceptional is the sheer completeness of the fossilized remains. Unlike Argentinosaurus, which was reconstructed from only a dozen bones, this titanosaur’s skeleton provides a far more comprehensive picture of its anatomy. Researchers found multiple individuals at the same site, offering a rare opportunity to study variations within the species. Analysis of the leg bones showed that the titanosaurs were young adults, still growing when they died, indicating that fully mature individuals might have been even larger.
The excavation site has been described by Dr. Pol as a “paleontological crime scene” due to its unique potential to yield new insights about these ancient creatures. The quality and quantity of the fossils found here are unparalleled, making it one of the most significant dinosaur discoveries of the modern era.
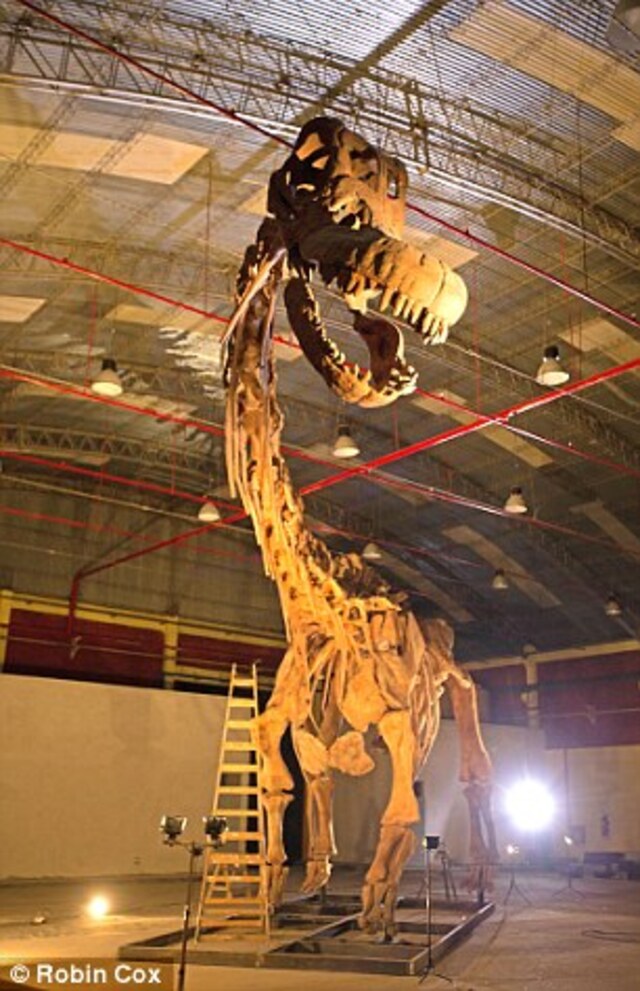

A life-sized model showcases the sheer scale of this colossal creature.
Scientific Analysis and Findings
Advanced forensic techniques were employed to study the fossils, revealing new details about the biology and behavior of titanosaurs. State-of-the-art graphics were used to create digital reconstructions of the dinosaur’s internal structure, illustrating how its organs and skeletal system functioned.

Cutting-edge graphics in the program will depict the internal anatomy of the dinosaur, demonstrating how its massive structure functioned, alongside captivating images of the fossils themselves.
These reconstructions showed how the dinosaur’s immense heart powered its body and how its long neck allowed it to reach vegetation high in the treetops. The size and condition of the fossils also helped refine estimates of the dinosaur’s weight and dimensions, confirming its status as the largest land animal ever discovered.
The Titanosaur’s Environment 102 Million Years Ago
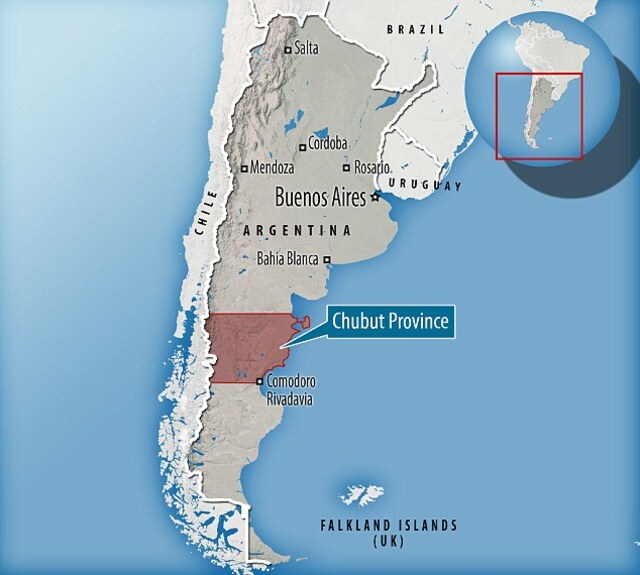
The fossils were uncovered at an excavation site on La Flecha Farm in Argentina’s Chubut Province, a barren expanse of desert terrain.
During the Cretaceous period, the region now known as Patagonia was a lush environment teeming with life. Dense forests, sprawling river systems, and an abundance of plant life made it an ideal habitat for herbivores like the titanosaur. The discovery of multiple individuals at La Flecha Farm suggests that these dinosaurs may have lived in herds, providing safety in numbers and ensuring access to food.
This find also sheds light on the evolutionary adaptations that allowed titanosaurs to thrive. Their enormous size likely served as a deterrent to predators, while their efficient digestive systems enabled them to process large quantities of low-nutrient vegetation.
The Journey from Fossil to Museum Display
Extracting and transporting the massive fossils from the remote desert location was no small feat. Some of the bones weighed over half a metric ton, requiring specialized equipment and careful planning. Once removed from the site, the fossils underwent cleaning and conservation to preserve them for study and display.
A collaborative effort between Canadian and Argentinian model makers resulted in the creation of a full-scale skeleton, now on display at a museum. This model, built using data from the fossils, allows visitors to appreciate the titanosaur’s sheer size and grandeur.
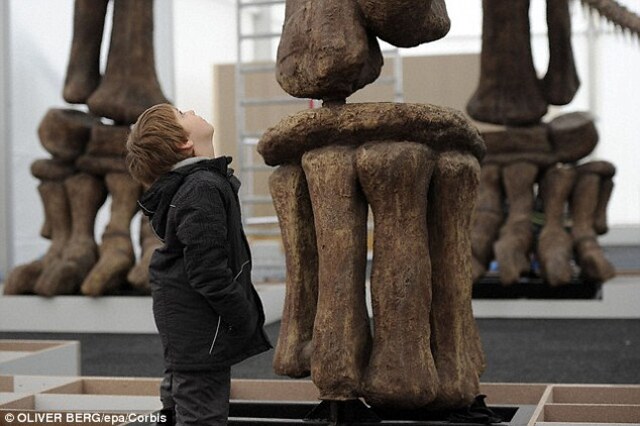

This newly identified species of vegetarian titanosaur, believed to be the largest land animal ever to walk the Earth, weighed an estimated 70 metric tons, surpassing the previous record holder, Argentinosaurus. A stock image shows a young boy marveling at an imposing 26-foot-tall (eight-meter) skeleton.
The Documentary: Attenborough and the Giant Dinosaur
The story of this remarkable discovery is chronicled in the BBC documentary Attenborough and the Giant Dinosaur, hosted by Sir David Attenborough. Filmed over two years, the program captures the excavation process, the scientific breakthroughs, and the challenges faced by the researchers. Using cutting-edge technology, the documentary brings the titanosaur to life, offering viewers a glimpse into its world.
One of the most striking moments in the documentary is the unveiling of the full-scale skeleton, a testament to the collaborative efforts of scientists, artists, and model makers. By combining science and storytelling, the program highlights the importance of paleontology in understanding Earth’s prehistoric past.
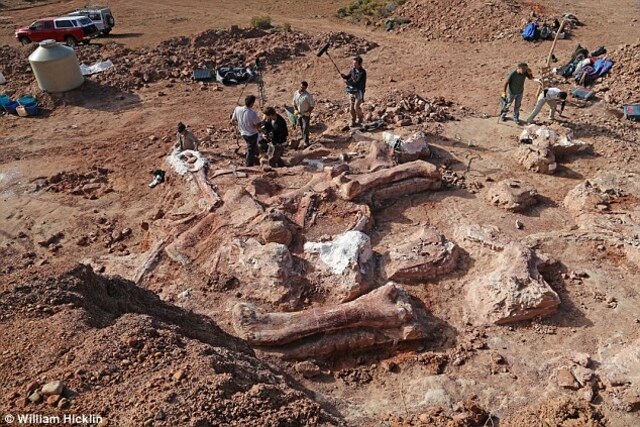

The documentary, set to air on BBC on 25 January, recounts how in 2014, a shepherd stumbled upon the tip of an enormous fossilized bone protruding from a rock in the Argentinian desert. The excavation site is featured prominently.
Impact on Science and Popular Culture
The discovery of the world’s largest dinosaur has captivated the public, inspiring renewed interest in paleontology and the Cretaceous period. It has expanded our understanding of titanosaurs, shedding light on their biology, behavior, and the ecosystems they inhabited.
This find also raises questions about the limits of size in land animals. How did these creatures sustain themselves? What evolutionary pressures led to their gigantism? As scientists continue to analyze the fossils, these questions may find answers, further enriching our knowledge of life on Earth.
Conclusion
The discovery of the world’s largest dinosaur at La Flecha Farm is a landmark moment in paleontology. By uncovering the remains of this titanosaur, researchers have not only rewritten the record books but also deepened our understanding of prehistoric life. From its massive heart to its towering frame, this gentle giant stands as a testament to the wonders of evolution and the mysteries that remain buried beneath our feet. As science continues to unravel the secrets of the past, the story of the titanosaur reminds us of the boundless possibilities of discovery.